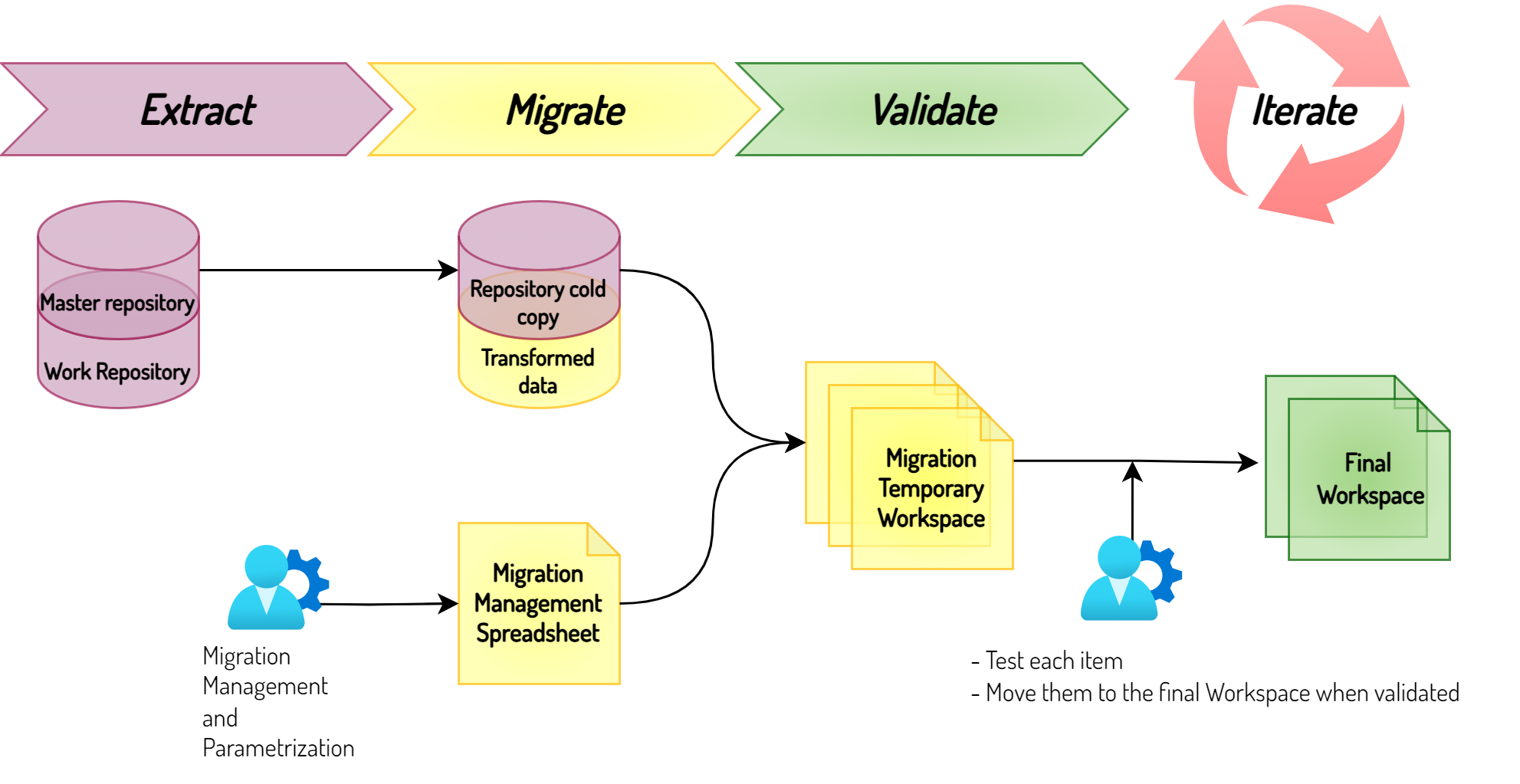
Many organizations today face significant challenges due to the use and adaptation of obsolete software, which often hinder agility and pose risks. The software lifecycle often sees the decline of initially promising and widely adopted solutions through a gradual reduction in market presence and support, superseded by other solutions, or the consolidation and reduction of advanced skills.
Despite the obvious disadvantages of maintaining outdated solutions, there is often a tendency to procrastinate or postpone the transition to new technology due to the considerable expenses involved and the typically high impacts on all involved systems. However, it is overlooked that the accumulated technological debt over time proliferates management and evolutionary costs. Additionally, it may happen suddenly (e.g., due to regulatory issues or end of life of software, etc.) that part of one’s platform still needs to be modernized, leading to much tighter timelines and higher risks.