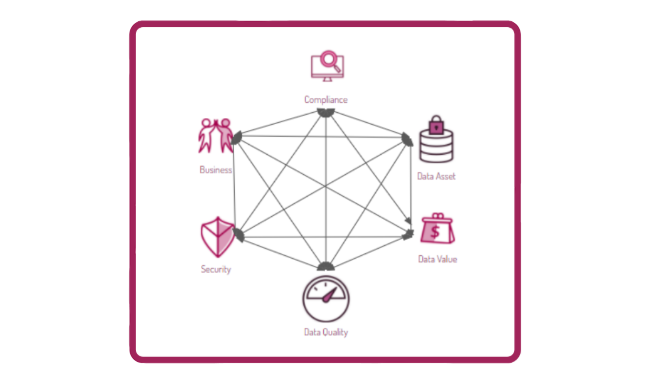
The centrality of data in business process management has led to a proliferation of Data Management initiatives, often dictated by contingencies and without a coherent vision.
Misunderstandings between IT and Business generate conflicting relationships that, especially in the most complex realities, can cause the Shadow IT phenomenon. This means the creation of Information Silos and duplication of information, increasing costs and decreasing Data Quality.
The importance of data (not only personal data) has come to the attention of national and supranational government authorities and criminal organizations; the lack of knowledge of Data Assets and data management processes can lead to a compliance deficit, with deleterious effects in terms of economics, security and image for companies.